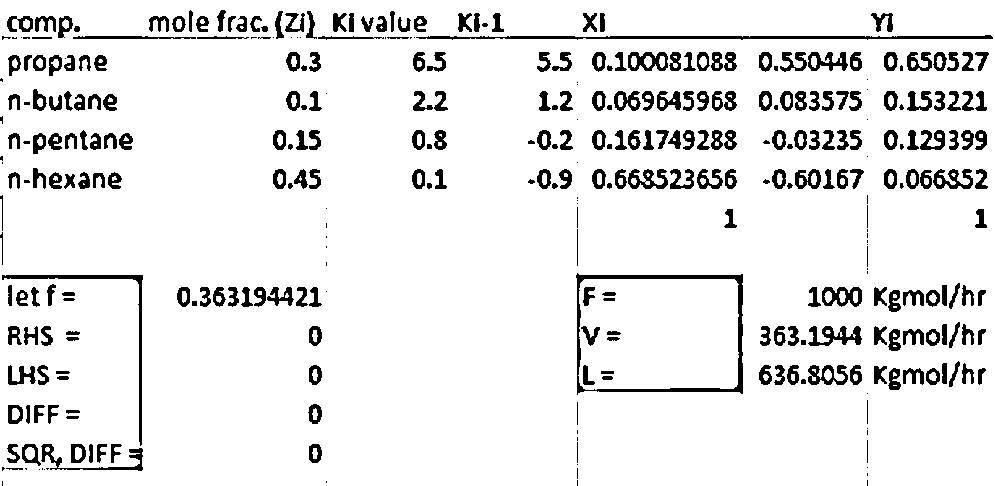
4. A flash chamber operating at 50 °C and 200 kPa is separating 1,000 kg moles/hr of a feed that is 30 mol % propane, 10 mol % n-butane, 15 mol % n-pentane, and 45 mol % n-hexane. Find the product compositions and flow rates. K-values for each chemical can be obtained using following equation. Constants for fitting are given in the attached table.
4. A flash chamber operating at 50 °C and 200 kPa is separating 1,000 kg moles/hr of a feed that is 30 mol % propane, 10 mol % n-butane, 15 mol % n-pentane, and 45 mol % n-hexane. Find the product compositions and flow rates. K-values for each chemical can be obtained using following equation. Constants for fitting are given in the attached table.
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Chapter33: Automated Methods Of Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 33.8QAP
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:4. A flash chamber operating at 50 °C and 200 kPa is separating 1,000 kg moles/hr of a feed that is
30 mol % propane, 10 mol % n-butane, 15 mol % n-pentane, and 45 mol % n-hexane. Find the
product compositions and flow rates. K-values for each chemical can be obtained using following
equation. Constants for fitting are given in the attached table.
= ari/T° +a7z/T+a7& +a, In p+a,2/p° +a„3/P
TABLE 2-3. Constants for fit to K values using Eq. (2-30)
Mean
Error
Сompound
Methane
-292,860
-600,076.875
8.2445
-8951
59.8465
1.66
Ethylene
7.90595
-84677 42.94594 0
2.65
Ethane
-687,248.25
7.90694
-88600
49.02654 0
1.95
Propylene
Propane
-923,484.6875 0
7.71725
-87871 47.67624 0
1.90
-970,688.5625 0
7.15059
-76984 0
6.90224
2.35
Isobutane
-1,166,846
7.72668
-92213 0
2.52
n-Butane
-1,280,557
7.94986
-96455 0
3.61
Isopentane -1,481,583
n-Pentane
7.58071
-93159 0
4.56
-1,524,891
7.33129
-89143 0
4.30
n-Hexane
-1,778,901
6.96783
-.84634 0
4.90
n-Heptane -2,013,803
6.52914
-.79543 0
6.34
n-Octane
-7646.81641 12.48457 -73152 0
7.58
n-Nonane
-2,551,040
5.69313
-67818 0
9.40
n-Decane
-9760.45703 13.80354 -71470 0
5.69
Note: Tis in R, and p is in psia
Source: McWilliams (1973)
Expert Solution
Step 1
Solution
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning