
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.1, Problem 3aT
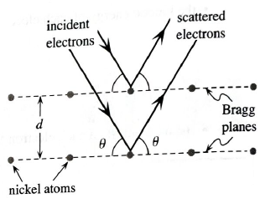
Use trigonometry to show that the path length difference between the two scattered beams shown is equal to
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Problem 9: For a Gaussian laser beam in air with a 0.5mm waist radius and X=850nm,
a. Find the (far field) diffraction half angle and the beam waist w(z) at z=50m
b. If the laser emits 5mW, what is the peak irradiance at z=50m?
c. What near field beam waist radius is required to limit the diffracted beam diameter to 1cm
at 50m? What detector diameter is needed to encircle (detect) 50% of the power?
B) Using the properties of F.T., Calculate the F.T. of the signal
sin (3πt) sin (5πt)
t²
x(t) = 5-
S1 and S2 in the figure below are effective point sources of radiation, excited by the same oscillator. They are coherent and in phase with eachother. Placed a distance d=4.17m apart, they emit equal amounts of power in the form of 1.06m wavelength electromagnetic waves. (a) Find the positions of the first, second, and third maxima of the received signal, as the detector D is moved along the x axis starting at 0. (b) Write an equation that you could use to find the location of any minima and find the position of at least one minimum on the x axis.
Chapter 14 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 14.1 - In the magnified view of the slits, an arrow is...Ch. 14.1 - For what values of the path length difference...Ch. 14.1 - Suppose that a single change were made to the...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 2aTCh. 14.1 - Prob. 2bTCh. 14.1 - Prob. 2cTCh. 14.1 - Use trigonometry to show that the path length...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 3bTCh. 14.2 - How does the voltmeter reading compare to the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 1bT
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Write each number in scientific notation.
3. 2650
Applied Physics (11th Edition)
12. FIGURE Q7.12 shows two masses at rest. The string is massless and the pullies are frictionless. The spring ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Nuclear fusion, the energy solute of Sun, hydrogen bombs, and fusion reactors, occurs much more readily when th...
University Physics Volume 2
With no gravity, a horizontally moving projectile follows a straight-line path. With gravity, how far below the...
Conceptual Integrated Science
You break a piece of Styrofoam packing material, and it releases lots of little spheres whose electric charge m...
Essential University Physics: Volume 2 (3rd Edition)
Express the unit vectors in terms of (that is, derive Eq. 1.64). Check your answers several ways Also work o...
Introduction to Electrodynamics
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Find inverse Laplace transform of S+3 5² +68+13arrow_forwardConsider one of the curves as shown. Suppose the intensity of the incident light is held fixed but its frequency is increased. Does the stopping potential as shown (a) remain fixed, (b) move to the right, or (c) move to the left?arrow_forwardThe parraled polazized from airilrointo wave travels dielect ric at Brewster angle o Develop calculate Er. and expression to 20arrow_forward
- Qualitatively sketch log(Ids) vs. Vg(assume Vds = Vdd) for the following Please pay attention to the positions of the curves relative to each other and label all curves.arrow_forwardNeeds Complete solution with 100 % accuracy. Otherwise skip if u can't give answer both of them. Thank you.arrow_forwardAn isotropic quasi-monochromatic point source radiates at a rate of 200 W. What is the propagating power density at a distance of 1m? What are the amplitudes of E- and B- fields at that point?arrow_forward
- Define the tunneling.arrow_forwardIn a cavity the total energy is u = a.V.T^4, where a is independent of V and T. Show that: F = -(aVT^4)/(3) + T.f(V) and S = (4aVT^4)/(3) - f(V), where f(V) is an unknown. Using the fact that S->0 for T->0. Show that the radiation pressure is P = U/(3V)arrow_forwardDetermine the backscattering energy loss factor (S) for the case of nonnormal incidence: incident beam at angle θ1 with respect to the sample normal and scattering angle θarrow_forward
- (a) Calculate the approximate wavenumber and wavelength of the fundamental absorption peak due to the stretching vibration of a carbonyl group C 0. (b) Focus the Practical Significance of Interferometer and Fourier Transform in FTIR.arrow_forwardWhat is the minimum angular spread of a 633-nmwavelength He-Ne laser beam that is originally 1.00 mm indiameter?(b) If this laser is aimed at a mountain cliff 15.0 km away, howbig will the illuminated spot be?(c) How big a spot would be illuminated on the Moon,neglecting atmospheric effects? (This might be done to hit acorner reflector to measure the round-trip time and, hence,distance.) Explicitly show how you follow the steps inProblem-Solving Strategies for Wave Opticsarrow_forward(a) What is the minimum angular spread of a 633-nm wavelength He-Ne laser beam that is originally 1.00 mm in diameter? (b) If this laser is aimed at a mountain cliff 15.0 km away, how big will the illuminated spot be? (c) How big a spot would be illuminated on the Moon, neglecting atmospheric effects? (This might be done to hit a corner reflector to measure the round-trip time and, hence, distance.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax
Polarization of Light: circularly polarized, linearly polarized, unpolarized light.; Author: Physics Videos by Eugene Khutoryansky;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8YkfEft4p-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY