
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337553292
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 7P
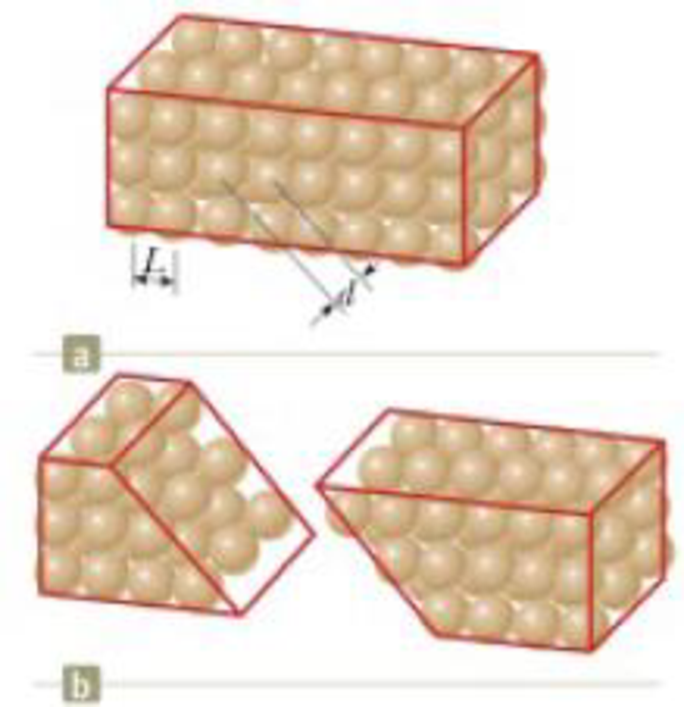
A crystalline solid consists of atoms stacked up in a repeating lattice structure. Consider a crystal as shown in Figure P1.7a. The atoms reside at the corners of cubes of side L = 0.200 nm. One piece of evidence for the regular arrangement of atoms comes from the flat surfaces along which a crystal separates, or cleaves, when it is broken. Suppose this crystal cleaves along a face diagonal as shown in Figure P1.7b. Calculate the spacing d between two adjacent atomic planes that separate when the crystal cleaves.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
7. A crystalline solid consists of atoms stacked up in a repeating lattice structure. Consider a crystal as shown in Figure P1.7a. The atoms reside at the corners of cubes of side L 5 0.200 nm. One piece of evidence for the regular arrangement of atoms comes from the flat surfaces along which a crystal separates, or cleaves, when it is broken. Suppose this crystal cleaves along a face diagonal as shown in Figure P1.7b. Calculate the spacing d between two adjacent atomic planes that sep- arate when the crystal cleaves.
The density of platinum is 21.45 x 103 kg/m3.
a. Calculate the volume (in m3/atom) occupied per platinum atom
b. Estimate the atomic diameter (in m);(The estimate uses the approximation that it is a cubic volume)
c. Using this estimation, calculate the thickness of a metal foil (in m) containing 2.0 x 101 atomic layers of platinum.
Grains of fine California beach sand are approximately spheres with an average radius of 70 μ m and are made of silicon dioxide. A solid cube of silicon dioxide with a volume of 1.00 m3 has a mass of 2600 kg. What mass of small sand grains would have a total surface area (the total area of all individual spheres) equal to the surface area of a cube 1.00 m on an edge?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Ch. 1.1 - In a machine shop, two cams are produced, one of...Ch. 1.3 - True or False: Dimensional analysis can give you...Ch. 1.4 - The distance between two cities is 100 mi. What is...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1PCh. 1 - Prob. 2PCh. 1 - Prob. 3PCh. 1 - Prob. 4PCh. 1 - You have been hired by the defense attorney as an...Ch. 1 - A surveyor measures the distance across a straight...Ch. 1 - A crystalline solid consists of atoms stacked up...
Ch. 1 - The position of a particle moving under uniform...Ch. 1 - Prob. 9PCh. 1 - (a) Assume the equation x = At3 + Bt describes the...Ch. 1 - A solid piece of lead has a mass of 23.94 g and a...Ch. 1 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 1 - Prob. 13PCh. 1 - Let AI represent the density of aluminum and Fe...Ch. 1 - One gallon of paint (volume = 3.78 103 m3) covers...Ch. 1 - Prob. 16PCh. 1 - (a) Compute the order of magnitude of the mass of...Ch. 1 - To an order of magnitude, how many piano tuners...Ch. 1 - Your roommate is playing a video game from the...Ch. 1 - How many significant figures are in the following...Ch. 1 - The tropical year, the time interval from one...Ch. 1 - Prob. 22PCh. 1 - Review. In a community college parking lot, the...Ch. 1 - Prob. 24PCh. 1 - Review. The ratio of the number of sparrows...Ch. 1 - Prob. 26PCh. 1 - Prob. 27PCh. 1 - Prob. 28PCh. 1 - Prob. 29APCh. 1 - Prob. 30APCh. 1 - The distance from the Sun to the nearest star is...Ch. 1 - Prob. 32APCh. 1 - Prob. 33APCh. 1 - A spherical shell has an outside radius of 2.60 cm...Ch. 1 - Air is blown into a spherical balloon so that,...Ch. 1 - In physics, it is important to use mathematical...Ch. 1 - The consumption of natural gas by a company...Ch. 1 - A woman wishing to know the height of a mountain...Ch. 1 - Prob. 39CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Perform the following arithmetic operations, keeping the correct number of significant figures in your answer. a. The product 56.2 0.154 b. The sum 9.8 + 43.4 + 124 c. The quotient 81.340/arrow_forwardFigure P1.6 shows a frustum of a cone. Match each of the three expressions (a) (r1 + r2)[h2 + (r2 r1)2]1/2, (b) 2(r1 + r2), and (c) h(r12 + r1r2 + r22)/3 with the quantity it describes: (d) the total circumference of the flat circular faces, (e) the volume, or (f) the area of the curved surface. Figure P1.6arrow_forwardYou are making a sculpture that is a pyramid with a square base . You want the height of the pyramid to be 4 inches less than the length of a side of the base . You want the volume of the sculpture to be 200 cubic inches . a . Let x represent the length ( in inches ) of a side of the sculpture's base . Draw a diagram of the sculpture , and label the dimensions in terms of x . b . Write a function that gives the volume V of the sculpture in terms of x .arrow_forward
- One mole of Gold (Au) atom has a mass of 197 g. We know that the density of gold is 19.30 g/cm3 in room temperature. Using those numbers, answer the following questions: a) What is the mass of a single gold atom in kg? b) Assume that gold atoms sit in a perfect cubic crystal structure. Estimate the distance between two gold atoms in meters. c) If we have a gold cube of 6 cm on each side, how many atoms can we fit along the edge of each side of the cube? d) What would be the mass, in kilograms, of the gold cube we discussed in part (c) (measuring 6 cm on each side)?arrow_forwardGrains of fine California beach sand are approximately spheres with an average radius of 50 m and are made of silicon dioxide, which has a density of 2600 kg/m3.What mass of sand grains would have a total surface area (the total area of all the individual spheres) equal to the surface area of a cube 1.00 m on an edge?arrow_forwardThe radius of an atom of gold (Au) is about 1.35 Å. How many gold atoms would have to be lined up to span 4.0 mm? Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forward
- A water molecule is shown schematically in the figure (Figure 1). The distance from the center of the oxygen atom to the center of a hydrogen atom is 0.96 Å, and the angle between the hydrogen atoms is 104.5 ∘. Find the center-to-center distance between the hydrogen atoms. (1Å=10−10m). r = ? Åarrow_forwardC L You are tasked with specifying the following structure. It is a cylinder attached to a sphere at one end. Unfortunately, you were not given all the dimensions. You know that the radius of the cylinder is one half (1/2) the radius of the sphere. What is the total volume of the structure as a function of the radius and length of the cylinder (you may neglect any excess volume at the join between sphere and cylinder). O a. V = πr²h+32r²/3 O b. V = r²(h+32r/3) O c. V = r²(th+32r/3) O d. V = r²(h+32/3)arrow_forwardA simple physics formula is density equals mass divided by volume. In problem 2 above, the density was δ(x,y,z) = e^((x^2+y^2+z^2)^3/2).The volume of the object could be calculated from the equations for volumes of spheres and cones with some simple subtraction. Why do we need to do a triple integral to find the mass of the solid? Why can’t we just use the physics formula M = ρ ·V ? Explain when we need a triple integral to calculate mass, and when we can get away with the simple physics formula. Most importantly, explain how the triple integral of p*dV uses the same physics formula and explain what the idea of an integral means.arrow_forward
- As an architect, you are designing a new house. A window has a height between 130 cm and 140 cm and a width between 64 cm and 60 cm. What is the largest area that the window could be?arrow_forwardA typical human cell is approximately 12.00 μm in diameter and enclosed by a membrane that is 9.000 nm thick. What is the volume of the cell including the membrane? To simplify the calculations, model the cell as a sphere. total volumetotal volume: ? What is the volume of the cell membrane? membrane volume: What percent of the total volume does its membrane occupy? membrane percentage:arrow_forwardThe Empire State building in New York City is approximately 1250 ft1250 ft tall. How many U.S. half dollars would be in a stack of the same height? Each half dollar is 2.15 mm2.15 mm thick.What is the value, in dollars, of the same stack of half dollars?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Components of a Vector (Part 1) | Unit Vectors | Don't Memorise; Author: Don't Memorise;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fwMUELxZ0Pw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
02 - Learn Unit Conversions, Metric System & Scientific Notation in Chemistry & Physics; Author: Math and Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W_SMypXo7tc;License: Standard Youtube License