
Concept explainers
Consider a book on top of a level table while the book is being pressed straight down by a hand.
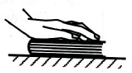
i. In the space below, draw a free-body diagram for the book. Label the forces as you did in the tutorial Forces.
ii. How do the forces exerted on the book in this case compare to the forces exerted on the book when the hand is not pushing? List any forces that are the same (i.e., same type of force, same direction, and same magnitude) in both cases. Make a separate list of forces that change (or are not present) when the hand is pressing down on the book.
iii. Is the magnitude of the weight equal to the magnitude of the normal force exerted by the table on the book? How can you tell?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
University Physics Volume 2
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
College Physics
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
- A horizontal force, F1, and a force F, acting at an angle of e to the horizontal, are applied to a block of mass m. The block is moving to the right at a constant velocity across a rough surface. Use Fk to denote the force of kinetic friction. Please use the interactive area below to draw the Free Body Diagram for the block. 1 Add Force O Reset All m Ftotal,x: Ftotal,y:arrow_forwardProblem 1: A block with a mass of m rests on a frictionless surface and is subject to two forces acting on it. The first force is directed in the negative x-direction. The second acts on the body at an angle 0 measured from horizontal, as shown. If necessary, use Fs and Fk for the forces of static and kinetic friction. L. F Please use the interactive area below to draw the Free Body Diagram for this block, assuming it is in static equilibrium. FBD : Fn, F1, Fg, F2, Fs, Fk, a, v 45, 0, 90, 135, 180, 225, 270, 315, 0 Force Labels: Angle Labels: m.arrow_forwardb. Draw and label a free body diagram (FBD) for each ball. (Don’t break any forces into components for the FBDs—save that work for the next question. Be sure your drawings show clearly any information you know about the directions and relative magnitudes of the forces.) Rank the relative magnitudes of all forces in your FBDs. (I’m looking for a single ranking that includes every different force in both FBDs, separated by <, >, or =.)Ball A: Ball B: * Among the two photos, Mag>N photo is the correct answer. The other pictures were solved by me(It's wrong). So please figure out for me what is wrong in my process and rewrite the solution as much as possible. Thank you.arrow_forward
- a. Upload a complete free body diagrams for Cart B as shown in the inclined plane diagram. Include all forces acting on Cart B. All forces must be labeled with two subscripts using the conventions defined in our lectures and in FlipIt Physics. The file you upload for this question must include ONLY a free body diagram for Cart B and NOTHING ELSE. No credit will be given for a large file that requires your instructor to find the answer to this question. Part of the point of this question is to understand what belongs in a free body diagram for Cart B. b. Using the forces that you defined in your free body diagram from the question above, write out Newton's Second Law as it applies to Cart B. All of the forces acting on Cart B must appear in your answer to this question, and they must appear with the subscripts and labels as defined by the conventions of our lectures and FlipIt Physics. Your equations should include only symbols (do not substitute numbers). You may need to write…arrow_forwardFind I and J values and please answer all parts of this question 1. Block 1 (3.5 kg) is resting on the surface of a table. On a sheet of paper, draw the free body diagram for block 1 using the two-subscript notation from class. After completing the free body diagram, enter below each force and its x & y-components. (use g = 10 m/s2) Remember that the x-component is the "i" component and the y-component is the "j" component. FORCES on BLOCK 1 Weight force on block 1 by Earth: 100 (two-subscript notation) The Weight on block 1 by the Earth has the notation: W1E. Value = ———i + ——- j N Remember that W1E points down (negative y-value) with a magnitude of m1 * g. Normal force on block 1 by Surface: (two-subscript notation) Value = ——i +——- j Narrow_forwardConsider the free body diagrams below. + The arrows represent forces. The direction of the arrow represents the direction of the force. The length of the arrow represent length of the arrows represents the strength of the force. Identify the diagram that is consistent with the following situation: A cable pulls a crate rightward at a constant speed across a horizontal surface. The surface provides a force that resists the crate's motion. B Provide an explanation for your choice. Darrow_forward
- Can you please draw the free body diagram of the problem? A mass of 10kg sits on a level surface. One end of the surface is raised until the block begins to slide down the ramp at a constant velocity and angle of 20⁰. a. What is the coefficient of friction between the block and the inclined plane? b. What is the weight of the Block,w? c. What is the Normal Force, N? d. What is the Frictional Force, Ff?arrow_forwardBlocks A and B are held on the palm of your outstretched hand as you lift them straight up atconstant speed. Assume mB>mA and that mhand=0.a. Draw separated free-body diagrams for A, B and your hand. Show all vertical forces andmake sure the vector lengths indicate the relative sizes of the forces.b. Rank in order from largest to smallest all of the vertical forces. Explain your reasoning.Now the hand is lifting the blocks so they have an upward acceleration.c. Draw separated free-body diagrams for A, B and your hand. Show all vertical forces andmake sure the vector lengths indicate the relative sizes of the forces.d. Rank in order from largest to smallest all of the vertical forces for when the block isaccelerating. Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardProblem 4: A crate sits on a rough surface. Using a rope, a man applies a force to the crate, as shown in the figure. The force is not enough to move the crate, however, and it remains stationary. Use f to represent the force of friction. Please use the interactive area below to draw the Free Body Diagram for the crate. L. y 1 Add Force S Reset All Ftotal,x: Ftotal.y:arrow_forward
- 3.2.2 Represent and reason Two blocks are connected with a light string that runs over two light pulleys.arrow_forwardIn rock climbing, various rope and pulley systems have been devised to help haul up heavy loads, including injured climbers. A rescuer is hauling up an injured climber who weighs 660 N using the rope and pulley system shown. (The ropes in this figure are drawn at various angles for clarity, but you can assume they’re all vertical.)a. What is the tension in rope 1, the rope that the rescuer pulls on?b. What is the tension in rope 2?arrow_forwardBlock 1 is removed without disturbing block 2. i. Consider the scenario where the mass m3 of block 3 is greater than the mass m2 of block 2. Without using equations, make a claim about the motion of block 3 in terms of balanced or unbalanced forces. ii. Derive an equation for the acceleration of block 3 for any arbitrary values of m3 and m2. Express your answer in terms of m3, m2, and physical constants as appropriate.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





