
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The empirical formula of the given acid has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Empirical formula of a compound is the smallest integer ratio of numbers of each element presented in that compound.
Molecular formula of a compound is integer multiple of empirical formula, the integer is depend upon the mass of empirical formula and the molecular mass of the compound.
The number of moles of any substance can be determined using the equation,
(a)
Answer to Problem 113SCQ
Empirical formula of the acid is
Explanation of Solution
Assuming the molecular formula of the compound is
It dissociates into carbondioxide and water. The equation is as follows.
Let’s calculate the moles of C in
Let’s calculate the moles of
Weight of Hydrogen =
Let’s calculate the weight of Oxygen:
Let’s calculate the mole of Oxygen:
Let’s calculate the mole ratio of each element:
Therefore, the empirical formula of the given compound is
(b)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula of the given acid has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two carboxylic acid groups.
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Empirical formula of a compound is the smallest integer ratio of numbers of each element presented in that compound.
Molecular formula of a compound is integer multiple of empirical formula, the integer is depend upon the mass of empirical formula and the molecular mass of the compound.
The number of moles of any substance can be determined using the equation,
(b)
Answer to Problem 113SCQ
Molecular formula of the acid is
Explanation of Solution
According to the law of gram equivalents, equivalent acid is equal to the equivalents of base.
Let’s calculate the molecular formula:
Substitute the ‘n’ value we get molecular formula of acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given acid has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two carboxylic acid groups.
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represent the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure indicates the all unpaired electrons present in the atom in the molecules.
The Lewis structure of Maleic is as follows.
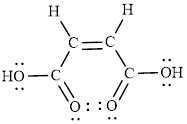
(d)
Interpretation:
The hybridization used by the carbon atom in the given acid compound has to be described.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two carboxylic acid groups.
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure indicates the all unpaired electrons present in the atom in the molecules.
The Lewis structure of Maleic is as follows.

The geometry around the entire carbon atoms in the molecule is trigonal planar, which means these carbon atoms used
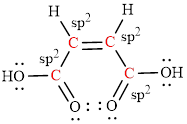
(e)
Interpretation:
The bond angles around each C-atom in the given molecule has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Maleic acid is prepared by the catalytic oxidation of benzene.It is a dicarboxylic acid ,that is, it has two carboxylic acid groups.
It is cis– isomer of butenedioic acid.Molecular formula is
The structure of maleic acid is as shown below.

Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure of Maleic is as follows.

The geometry around the entire carbon atoms in the molecule is trigonal planar, which means these carbon atoms used

The geometry around each carbon atom in the given compound is trigonal planar and so the bond angle is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- TRUE OR FALSE (a) A functional group is a group of atoms in an organic molecule that undergoes a predictable set of chemical reactions. (b) The functional group of an alcohol, an aldehyde, and a ketone have in common the fact that each contains a single oxygen atom. (c) A primary alcohol has one —OH group, a secondary alcohol has two —OH groups, and a tertiary alcohol has three —OH groups. (d) There are two alcohols with the molecular formula C3H8O. (e) There are three amines with the molecular formula C3H9N. (f) Aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters all contain a carbonyl group. (g) A compound with the molecular formula of C3H6O may be either an aldehyde, a ketone, or a carboxylic acid. (h) Bond angles about the carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde, a ketone, a carboxylic acid, and an ester are all approximately 109.5°. (i) The molecular formula of the smallest aldehyde is C3H6O, and that of the smallest ketone is also C3H6O. (j) The molecular formula of the smallest carboxylic…arrow_forwardExplain the reaction between Methyl Salicylate with acetyl chloride (CH3COCl). Gives your answer in detail from the name of the reaction until the formation of the product. You are advised to give an illustration of the reaction.arrow_forwardPolychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) are chemicals formed by attaching one or more chlorine atoms to a pair of connected benzene rings. (a) Summarise the adverse health effects associated with exposure to PCBs. (b) With a suitable illustration, explain the action of PCBs toxicity.arrow_forward
- (a) Discuss the feature of ionic and covalent bond. (b) Explain bonding of methanol in terms of hybridization.arrow_forward(b) Differentiate between bioethanol and biodiesel.arrow_forward(a) When the metallic element sodium combines with the nonmetallic element bromine, Br2(l), how can you determine the chemical formula of the product? How do you know whether the product is a solid, liquid, or gas at room temperature? Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction. (b) When a hydrocarbon burns in air, what reactant besides the hydrocarbon is involved in the reaction? What products are formed? Write a balanced chemical equation for the combustion of benzene C6H6(l), in air.arrow_forward
- (a) What is the difference between chlorofluorocarbons and hydrofluorocarbons?arrow_forwardWrite a balanced chemical equation based on the following description: propanol, C₃H₇OH(l) burns in airarrow_forward. (a) The insecticide methoprene (see Fig. 7.32d) is an ester. Write the structural formulas for the alcohol and the carboxylic acid that react to form it. Name the alcohol.(b) Suppose that the carboxylic acid from part (a) is changed chemically so that the OCH3 group is replaced by a hydrogen atom and the COOH group is replaced by a CH3 group. Name the hydrocarbon that would result.arrow_forward
- Alcohols can be produced by the hydration of:(a) Alkenes(b) alkynes(c) alkanes(d) acidsarrow_forward(a) Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the combustion of 1 mol of benzene, C6H61l2, to CO21g2 and H2O1l2.(b) Compare the quantity of heat produced by combustion of 1.00 g propane with that produced by 1.00 g benzene.arrow_forwardThere are two different butanoic acids with the formula C5H10O2. Draw and name them.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





