
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 36, Problem 49PQ
Problems 49 and 50 are paired.
C Optical flats are flat pieces of glass used to determine the flatness of other optical components. They are placed at an angle above the component as shown in Figure P36.49A, and monochromatic light is incident and observed from above, leading to interference fringes. Parts B and C of Figure P36.49 show the results of tests on two optical components. Which of the two is more flat? Explain.
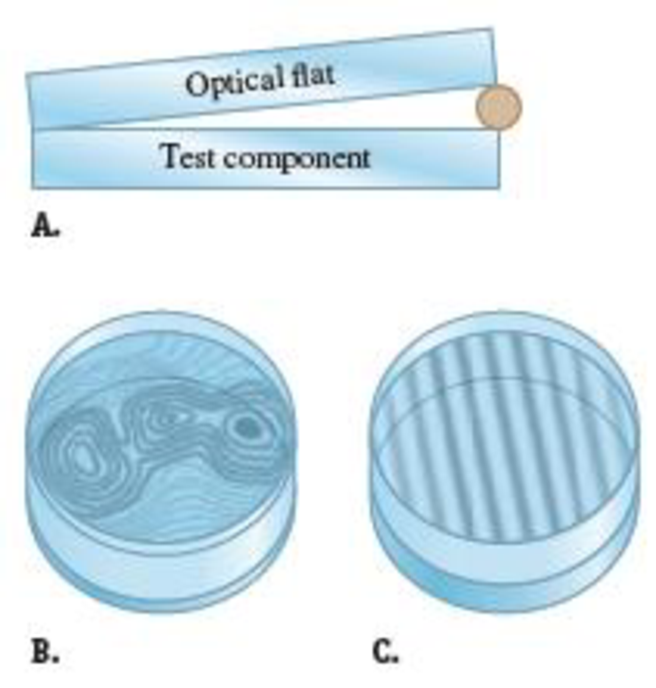
Figure P36.49 Problems 49 and 50.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
A helium-neon laser (λ = 633 nm), as shown, is built with a glass tube of inside diameter 1.0 mm. One mirror is partially transmitting to allow the laser beam out. An electrical discharge in the tube causes it to glow like a neon light. From an optical perspective, the laser beam is a light wave that diffracts out through a 1.0-mm-diameter circular opening.a. Explain why a laser beam can’t be perfectly parallel, with no spreading.b. The angle θ1 to the first minimum is called the divergence angle of a laser beam. What is the divergence angle of this laser beam?c. What is the diameter (in mm) of the laser beam after it travels 3.0 m?d. What is the diameter of the laser beam after it travels 1.0 km?
4. a. Determine the size of the Airy disk (in m) found at the center of a 4.00-cm diameter
lens, with a focal length of 15.0 cm. Assume the incident light wavelength is the middle of
the visible spectrum = 550. nm.
b. In observational astronomy, we assume that stars, being so far away, are point sources of
light, and that the image of a star in a telescope eyepiece is therefore also a point. Given
that the average human near-field resolution is 0.10 mm, does your result in part a justify
this assumption? Explain your answer, using the value from part a.
c. Assume that the objective lens diffraction limit is the only one that matters on a
telescope (actually a good assumption, not justified here). What is the angular size (in
radians) of the smallest object that can be truly observed as a disk on the 4.00-cm telescope
in part a? Can Jupiter (maximum angular size = 51 arc-seconds) be seen as a disk through
this telescope? Note that real telescopes have glass or mirror imperfections which…
A photographer is attempting to take a photo of two ships on the horizon which are separated by a distance L = 1.3 m. The camera has an aperture of D = 1.2 cm. Assume the range of visible light is 400 nm - 700 nm.
A. Find the minimum angle of resolution in degrees.
B. What is the maximum distance, in meters, that the ships can be from the photographer to get a resolvable picture?
Chapter 36 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
Ch. 36.2 - Prob. 36.1CECh. 36.3 - Prob. 36.2CECh. 36.4 - Prob. 36.3CECh. 36.5 - Prob. 36.4CECh. 36.5 - Prob. 36.5CECh. 36 - Many circular apertures are adjustable, such as...Ch. 36 - Many of the images we regularly look at are...Ch. 36 - The hydrogen line at 1420.4 MHz corresponds to the...Ch. 36 - Prob. 4PQCh. 36 - Estimate the diffraction-limited resolution of the...
Ch. 36 - Prob. 6PQCh. 36 - Prob. 7PQCh. 36 - Prob. 8PQCh. 36 - Prob. 9PQCh. 36 - Prob. 10PQCh. 36 - Prob. 11PQCh. 36 - Prob. 12PQCh. 36 - Prob. 13PQCh. 36 - Prob. 14PQCh. 36 - Prob. 15PQCh. 36 - Prob. 16PQCh. 36 - Prob. 17PQCh. 36 - Prob. 18PQCh. 36 - Prob. 19PQCh. 36 - Prob. 20PQCh. 36 - Prob. 21PQCh. 36 - Prob. 22PQCh. 36 - Prob. 23PQCh. 36 - Prob. 24PQCh. 36 - Light of wavelength 566 nm is incident on a...Ch. 36 - Prob. 26PQCh. 36 - Prob. 27PQCh. 36 - Prob. 28PQCh. 36 - Prob. 29PQCh. 36 - Prob. 30PQCh. 36 - A light source emits a mixture of wavelengths from...Ch. 36 - Prob. 32PQCh. 36 - Prob. 33PQCh. 36 - Prob. 34PQCh. 36 - Prob. 35PQCh. 36 - Prob. 36PQCh. 36 - Prob. 37PQCh. 36 - Prob. 38PQCh. 36 - Prob. 39PQCh. 36 - Prob. 40PQCh. 36 - Prob. 41PQCh. 36 - Prob. 42PQCh. 36 - Prob. 43PQCh. 36 - Prob. 44PQCh. 36 - CASE STUDY Michelsons interferometer played an...Ch. 36 - CASE STUDY Michelsons interferometer played an...Ch. 36 - Prob. 47PQCh. 36 - Prob. 48PQCh. 36 - Problems 49 and 50 are paired. C Optical flats are...Ch. 36 - Optical flats are flat pieces of glass used to...Ch. 36 - Prob. 51PQCh. 36 - Prob. 52PQCh. 36 - Figure P36.53 shows two thin glass plates...Ch. 36 - Viewed from above, a thin film of motor oil with...Ch. 36 - Newtons rings, discovered by Isaac Newton, are an...Ch. 36 - Prob. 56PQCh. 36 - What is the radius of the beam of an argon laser...Ch. 36 - Prob. 58PQCh. 36 - A diffraction grating with 428 rulings per...Ch. 36 - How many rulings must a diffraction grating have...Ch. 36 - Prob. 61PQCh. 36 - White light is incident on a diffraction grating...Ch. 36 - X-rays incident on a crystal with planes of atoms...Ch. 36 - Prob. 64PQCh. 36 - Prob. 65PQCh. 36 - Prob. 66PQCh. 36 - The fringe width b is defined as the distance...Ch. 36 - The fringe width is defined as the distance...Ch. 36 - Prob. 69PQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Figure P35.24 shows the diffraction patterns produced by a slit of varying width. What is the relative width of the slit in each case, from narrowest to widest? FIGURE P35.24 Problems 24 and 32.arrow_forwardFigure P38.10 on the next page shows a monochromatic beam of light of wavelength 575 nm incident on a slab of crown glass surrounded by air. Use a protractor to measure the angles of incidence and refraction. a. What is the speed of the beam of light within the glass slab? b. What is the frequency of the beam of light within the glass slab? c. What is the wavelength of the beam of light within the glass slab? FIGURE P38.10arrow_forwardThe lens of a telescope has a diameter of 25 cm. You are using it to look at two stars that are 2 × 10 17 m away from you and 6 × 10 9 m from each other. You are measuring light with a wavelength of 700 nm. As the light goes through the lens, it diffracts. a. Is it possible, using this telescope, to see the two stars as separate stars? b. What is the minimum possible lens diameter you would need in order to resolve these two stars?arrow_forward
- Consider a light wave passing through a slit and propagating toward a distant screen. Figure P37.53 shows the intensity variation for the pattern on the screen. Give a mathematical argument that more than 90% of the transmitted energy is in the central maximum of the diffraction pattern. Sugges- tion: You are not expected to calculate the precise percent- age, but explain the steps of your reasoning. You may use the identification 1 1 8 Imax asine -3T -27 -T 27 37 A Figure P37.53 ||arrow_forwardA telescope can be used to enlarge the diameter of a laser beam and limit diffraction spreading. The laser beam is sent through the eyepiece and out the objective, and can then be projected onto a satellite or the Moon. a. If this is done with the Mount Wilson telescope, producing a 2.1 m diameter beam of 690 nm light, what is the minimum angular spread, in radians, of the beam? b. Neglecting atmospheric effects, what is the diameter of the spot this beam would make on the Moon, assuming a lunar distance of 3.84×108 m?arrow_forward35. Figure P36.35 shows a radio-wave transmitter and a receiver separated by a distance d - 50.0 m and both a distance A - 35.0 m above the ground. The receiver can receive sig- nals both directly from the transmitter and indirectly from signals that reflect from the ground. Assume the ground is level between the transmitter and receiver and a 180° phase shift occurs upon reflection. Determine the longest wave- lengths that interfere (a) constructively and (b) destructively. Transmitter Recriver Figure P36.35 Problems 35 and 36.arrow_forward
- The walls of a soap bubble have about the same index of refraction as that of plain water, n=1.33. There is air both inside and outside the bubble. a. What wavelength (in air) of visible light is most strongly reflected from a point on a soap bubble where its wall is 288 nm thick? b. What wavelength (in air) of visible light is most strongly reflected from a point on a soap bubble where its wall is 346 nm thick?arrow_forwardA. An x-ray beam with wavelength 0.130 nm is directed at a crystal. As the angle of incidence increases, you observe the first strong interference maximum at an angle 62.0∘. What is the spacing d between the planes of the crystal? Express your answer in nanometers to three significant figures. B.Find the angle θ2 at which you will find a second maximum. Express your answer in degrees to three significant figures.arrow_forwardA laser beam with wavelength λ = 675 nm hits a grating with n = 4750 grooves per centimeter. A. Calculate the grating spacing, d, in centimeters. B. Find the sin of the angle, θ2, at which the 2nd order maximum will be observed, in terms of d and λ. C. Calculate the numerical value of θ2 in degrees.arrow_forward
- 36. Figure P36.35 shows a radio-wave transmitter and a receiver separated by a distance d and both a distance h above the ground. The receiver can receive signals both directly from the transmitter and indirectly from signals that reflect from the ground. Assume the ground is level between the transmitter and receiver and a 180* phase shift occurs upon reflection. Determine the longest wavelengths that interfere (a) constructively and (b) destructively.arrow_forwardMirror M₁ in the figure below is moved through a displacement AL. During this displacement, 248 fringe reversals (formation of successive dark or bright bands) are counted. The light being used has a wavelength of 631.4 nm. Calculate the displacement AL. μm A single ray of light is split into two rays by mirror Mo, which is called a beam splitter. Telescope As M₁ is moved, an interference pattern changes in the field of view. Light source L₂ M₂ Mo 4₁ The path difference between the two rays is varied with the adjustable mirror M₁. M₁arrow_forwardIn Figure P37.18, let L = 120 cm and d = 0.250 cm. The slits are illuminated with coherent 600-nm light. Calculate the distance y from the central maximum for which the average intensity on the screen is 75.0% of the maximum.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Spectra Interference: Crash Course Physics #40; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-ob7foUzXaY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY