
Concept explainers
a)
The resolved shear stress acting on the
a)
Answer to Problem 52AAP
The resolved shear stress acting on the
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the Schmidt’s law:
Here,
Conclusion:
Draw the schematic diagram of slip plane and direction of the (111)
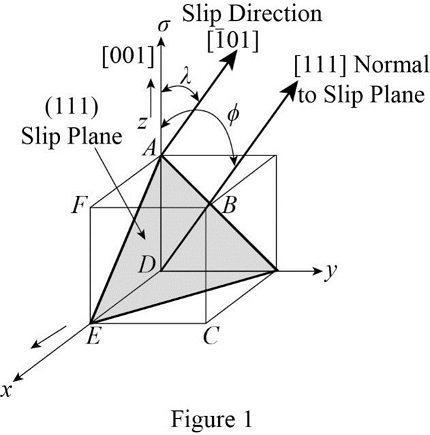
Draw the geometry of slip plane (
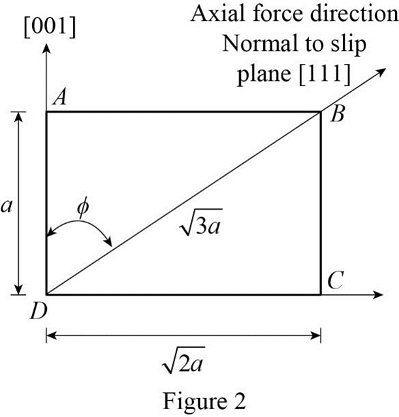
Draw the geometry of slip plane (
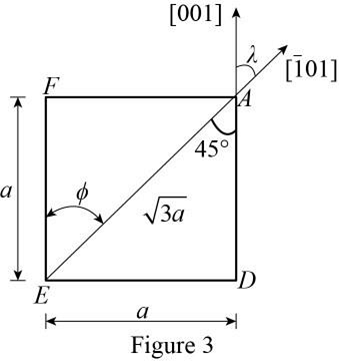
The miller indices of the crystal plane and the direction indices of the normal to a crystal plane are same in the cubic system.
Use the figure (3), if the line AE is bisected the the [001] plane then calculate the angle of EAD.
Calculate the angle between the uniaxial force and normal to the slip plane using the Figure 2.
Substitute
Thus, the resolved shear stress acting on the (111)
b)
The resolved shear stress acting on the
b)
Answer to Problem 52AAP
The resolved shear stress acting on the
Explanation of Solution
Draw the schematic diagram of slip plane and direction of the (111)
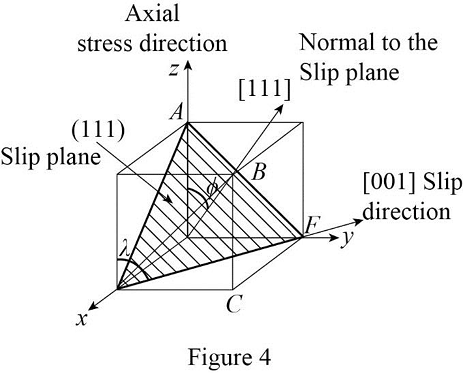
Draw the geometry of slip plane (
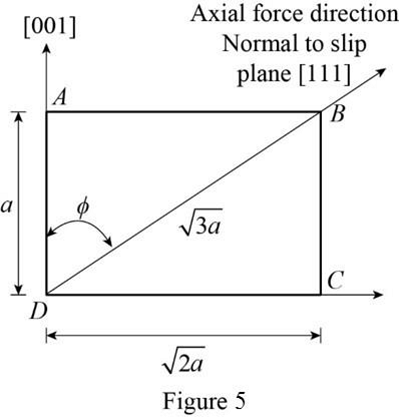
Refer the Figure 5, the angle between the (111) and [111] are
Calculate the angle between the axial plane [001] and normal slip plane [111]
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the resolve shear stress acting on the (111)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Foundations of Materials Science and Engineering
- A single crystal of a metal that has the FCC crystal structure is oriented such that a tensile stress is applied parallel to the [100] direction. If the critical resolved shear stress for this material is 1.18 MPa, calculate the magnitude of applied stress necessary to cause slip to occur on the (111) plane in the [1-10] direction.arrow_forwardConsider a single crystal of silver oriented such that a tensile stress is applied along a [001] direction. If slip occurs on a (111) plane and in a 101 direction, and is initiated at an applied tensile stress of 1.1 MPa (160 psi), compute the critical resolved shear stress. i MPаarrow_forwardAn FCC crystal is pulled in tension along the [100] direction. (a) Determine the Schmid factor for all slip systems. (b) Identify the slip system(s) that would be activated first. (c) What is the tensile stress under which this crystal will flow plastically? (t. = 50 MPa)arrow_forward
- Help me pleasearrow_forwardConsider a single crystal of BCC iron oriented such that tensile stress is applied along a[010] direction. Compute the resolved shear stress along a (110) plane and in a [1⃑ 1 1]direction when a tensile stress of 50 MPa is applied. If Slip occurs on a (110) plane and ina [1⃑ 1 1] direction and the critical resolved shear stress is 25 MPa, calculate themagnitude of the applied tensile stress necessary to initiate yielding.arrow_forwardA single crystal of a metal that has the FCC crystal structure is oriented such that a tensile stress is applied parallel to the [110] direction. If the critical resolved shear stress for this material is 1.75 MPa, calculate the magnitude(s) of applied stress(es) necessary to cause slip to occur on the (111) plane in each of the [110], [101] and [011] directions.arrow_forward
- 5. Consider a single crystal of some hypothetical metal that has the FCC crystal structure and is oriented such that a tensile stress is applied along a [102] direction. If slip occurs on a (111) plane and in a [101] direction, compute the stress at which the crystal yields if its critical resolved shear stress is 3.42 MPa.arrow_forwardA single crystal of an FCC metal isoriented so that the [001] direction is parallel to an applied stress of 5000 psi. Calculate the resolved shear stress acting on the (111) slip plane in the [110] and [101] slip directions. Which slip system(s) will become active first?arrow_forwardA single-crystal rod of FCC nickel is oriented with the [001] direction parallel to the rod axis. a. Identify the type of slip system involved in the plastic flow of nickel. b. How many such slip systems are in a position to be activated at the same time when the load is applied parallel to this crystallographic direction? c. What is the Schmid factor for this slip system? (The angles between the {100} and {110} and {100} and {111} planes are 45 and 54.7°, respectively.)arrow_forward
- Sometimes, in the equation for resolved shear stress in a single crystal, the term cos cos is termed the Schmid factor. Determine the magnitude of the Schmid factor for an FCC single crystal oriented with its [100] direction parallel to the loading axis.arrow_forwardA single crystal of FCC metal is oriented so that the [001] direction is parallel to an applied stress of 5000 psi. Calculate the resolved shear stress on the (111) slip plane in the [1bar 10] and [01bar 1] slip directions.arrow_forwardA single crystal of an FCC metal is oriented so that the [001] direction is parallel to an applied stress of 5000 psi. Calculate the resolved shear stress acting on the (111) slip plane in the [-110], and [10-1] slip directions. Which slip system(s) will become active first?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





