
Concept explainers
Absorption Costing Approach to Cost-Plus Pricing LO6—8
Martin Company uses the absorption costing approach to cost-plus pricing. It is considering the introduction of a new product. To determine a selling price, the company has gathered the following information:
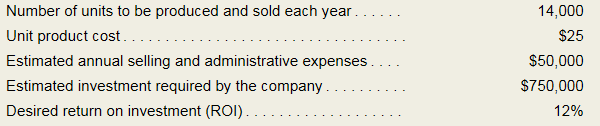
Required:
- Compute the markup percentage on absorption cost required to achieve the desired ROL.
- Compute the selling price per unit.
Concept Introduction:
Costing is a process of calculation of the cost of the product or service manufactured or provided by an organization. There are two methods of costing; absorption costing and variable costing.
As per nature, costs can be divided into three categories, i.e., variable costs, fixed costs, and mixed costs.
Requirement-1:
The markup percentage.
Answer to Problem 6A.1E
The markup percentage is 25.71%.
Explanation of Solution
The markup percentage is calculated as follows:
| Number of units (A) | $ 14,000 |
| Unit product cost (B) | $ 25 |
| Total absorption product cost (C) = (A*B) | $ 350,000 |
| Selling and admn expenses (D) | $ 50,000 |
| Total Cost (E) = (C+D) | $ 400,000 |
| Amount of investment (F) | $ 750,000 |
| Desired return on investment (G) | 12% |
| Desired markup (H) = (F*G) | $ 90,000 |
| Markup % (I) = (H/C) | 25.71% |
Concept Introduction:
Costing is a process of calculation of the cost of the product or service manufactured or provided by an organization. There are two methods of costing; absorption costing and variable costing.
As per nature, costs can be divided into three categories, i.e., variable costs, fixed costs, and mixed costs.
Requirement-2:
The selling price per unit.
Answer to Problem 6A.1E
The selling price per unit is $35.
Explanation of Solution
The selling price per unit is calculated as follows:
| Number of units (A) | $ 14,000 |
| Unit product cost (B) | $ 25 |
| Total absorption product cost (C) = (A*B) | $ 350,000 |
| Selling and admn expenses (D) | $ 50,000 |
| Total Cost (E) = (C+D) | $ 400,000 |
| Amount of investment (F) | $ 750,000 |
| Desired return on investment (G) | 12% |
| Desired markup (H) = (F*G) | $ 90,000 |
| Markup % (I) = (H/C) | 25.71% |
| Tota cost per unit (J) = (E/A) | $ 28.57 |
| Markup per unit (K) = (H/A) | $ 6.43 |
| Selling price (J+K) | $ 35.00 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- If a company chooses a price to charge for its product by adding up all the expenses necessary to make the product and then adding in a profit, this is known as: a) Target Costing Ob) Skimming Pricing Oc) Cost-Based Pricing Od) Odd-Even Pricing Oe) Penetration Pricingarrow_forwardG http Chapter Review My... Sales price Contribution margin ratio Fixed costs Tra.. Vernon Company reported the following data regarding the product it sells: a. Break-even point in dollars a. Break-even point in units b. Sales in dollars b. Sales in units c. Break-even point in dollars c. Break-even point in units $60 Man... $ 10% $216,000 M Questio... Required Use the contribution margin ratio approach and consider each requirement separately. b Ans... 2,160,000 36,000 Bes... Saved a. What is the break-even point in dollars? In units? b. To obtain a profit of $54,000, what must the sales be in dollars? In units? c. If the sales price increases to $72 and variable costs do not change, what is the new break-even point in dollars? In units? US fron.arrow_forwardCost Plus Pricing This is the most common cost-based approach to pricing a product, in which a marketer figures all costs for the product and then adds an amount to cover profit. In some cases, any costs of doing business that are not assigned to specific products. The most frequently used type of cost-plus pricing is straight markup pricing. The price is calculated by adding a predetermined percentage to the cost. Most retailers and wholesalers use markup pricing exclusively because of its simplicity - users need only estimate the unit cost and add the markup. The first step requires that the unit cost be easy to estimate accurately and that production rates are fairly consistent. We assume that a jeans’ manufacturer has fixed costs (the cost of the factory, advertising, managers’ salaries, etc.) of $2,000,000. The variable cost for a pair of jeans (the cost of fabric, zipper, thread, and labor) is $20.00. With the current plant, the firm can produce a total of 400,000 pairs of…arrow_forward
- Total cost method of product pricing Based on the data presented in Exercise 17, assume that Smart Stream Inc. uses the total cost method of applying the cost-plus approach to product pricing. A. Determine the total costs and the total cost amount per unit for the production and sale of 10,000 cellular phones. B. Determine the total cost markup percentage (rounded to two decimal places) for cellular phones. C. Determine the selling price of cellular phones. (Round markup to the nearest dollar.)arrow_forwardThe absorption costing approach to cost-plus pricing is the safest method to use regardless of unit sales considers customer demand for the product relies on forecasted unit sales assumes that customers will pay whatever price the company decides to charge makes pricing look simplearrow_forwardEvaluate the quantity at which revenue equals to costs (break-even point). <use Goal seek> Assumptions: Fixed cost: 5000 Material costs per item: 2.25 Labor costs per item: 6.5 Shipping costs per 100 items: 200 Price per item: 12.99arrow_forward
- Under absorption costing, how is it possible to increase net operating income without increasing sales? Post 150 word minimum discussion question answer.arrow_forward8:15 1) Assume that no changes are made to the selling price or costs, calculate the amount of units that Thermo Blast must sell: a. To breakeven (3 Marks) b. To attain the estimated net profit (7 Marks) 2) Determine the alternative that Thermo Blast should select to achieve its Net profit goal. (15 Marks) Part B 3) By reference to the above data, explain: a. Variable costs in the context of cost-volume-profit (CPV) analysis? (5 Marks) b. Fixed costs in the context of CPV analysis? (5 Marks) c. Contribution margin in the context of CPV analysis? (5 Marks) Problem Set 2 Carrie's Limited has two departments, the assembly department and the testing department in its brake-pad manufacturing plant, where each brake-pad is conveyed through each department. Carrie's process-costing system consist of two cost categories: Single direct cost (direct materials) and a single indirect-cost category (conversion costs). Direct materials are added at the beginning of the process. Conversion costs are…arrow_forwardFollowing information is related to Product X of Zempa Company: Current replacement cost Cost to distribute Historical cost Normal profit margin Selling price $230 $42 $215 $36 $245 If lower-of-cost-or-market rule (LCM Rule) is applied, then the value of Product X that would be reported in the balance sheet is: a. $215 b. $230 c. $203 d. $167arrow_forward
- Chapter 3- CVP Cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis requires an understanding of cost behavior: variable and fixed costs. Cost behavior differs from the GAAP-based financial reporting focus: product and period costs. The two ways to categorize costs results in TWo different income statements: Absorption costing income statement: S-C-GM-SA-NI (Key assumption: Split costs into product and period costs) Variable costing income statement: S-VE-CM-FE-NI (Key assumption: Split costs into variable and fixed) 1. 2. Absorption Costing Income Statement Variable Costing Income Statement Sales $500,000 Sales $500,000 Less: Variable expenses Less: Cost of goods sold: Variable (DM+DL+VOH) Fixed (FOH) Gross margin 100,000 Product costs 100,000 60,000 S&A costs 110,000 340,000 Contribution margin 290,000 Less: Fixed expenses Less: Selling & administrative Variable 110,000 Product costs 60,000 Fixed 140,000 S&A costs 140,000 Taxable income $90,000 Taxable income $90,000 LINK THE LINEAR COST FUNCTION TO…arrow_forwardWhat selling price will earn a gross profit of P 2.50 per unit under absorption costing?arrow_forwardIdentification of variable, semi-variable, and fixed costs.*Provide total VC/unit, total FC, and Semi-VC here as well. q 1. Breakeven in units. q 2. Breakeven in Sales q 3. Units including Target profit q 4. Income statement as at Dec.31, 202x V&A Carpet cleaning (Finney Franchise) based on units from Q3 with target profitarrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
