
(a)
Interpretation: The major product and mechanism needs to be determined in the given reaction.
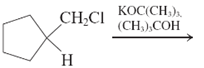
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an
(b)
Interpretation: The major product and mechanism needs to be determined in the given reaction.
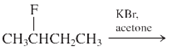
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(c)
Interpretation: The major product and mechanism needs to be determined in the given reaction.
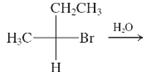
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(d)
Interpretation: The major product and mechanism needs to be determined in the given reaction.
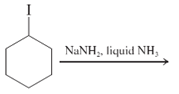
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(e)
Interpretation: The major product and mechanism needs to be determined in the given reaction.
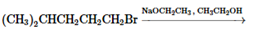
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(f)
Interpretation: The major product and mechanism needs to be determined in the given reaction.
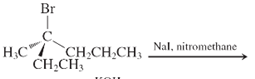
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(g)
Interpretation: The major product and mechanism needs to be determined in the given reaction.
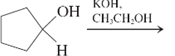
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(h)
Interpretation: The major product and mechanism needs to be determined in the given reaction.
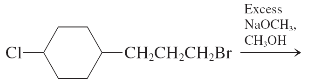
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(i)
Interpretation: The major product and mechanism needs to be determined in the given reaction.
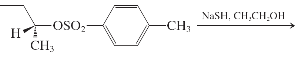
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(j)
Interpretation: The major product and mechanism needs to be determined in the given reaction.
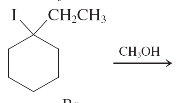
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(k)
Interpretation: The major product and mechanism needs to be determined in the given reaction.
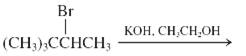
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(l)
Interpretation: The major product and mechanism needs to be determined in the given reaction.
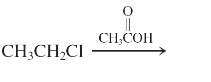
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- All rearrangements we have discussed so far have involved generation of an electron-deficient carbon followed by a 1,2-shift of an atom or a group of atoms from an adjacent atom to the electron-deficient carbon. Rearrangements by a 1,2-shift can also occur following the generation of an electron-deficient oxygen. Propose a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed rearrangement of cumene hydroperoxide to phenol and acetone.arrow_forwardCompound A reacts with the reagents shown in the image. Write the mechanism, step by step, for the formation of product B. Note that B has the molecular formula C14 H18 O.arrow_forwardCS41 10.) Chapter 7: E2 SNI + EI SN1+ E1 Mechanisms. Using correct mechanistic arrows, provide the step-by-step mechanism that demonstrates how the following reactions proceed to afford both substitution and elimination products via SN1 and E1. You do not need to show stereochemistry while providing the mechanism, but show correct stereochemistry in the final product(s). If there is more than one product feel free to write +E or +D as appropriate (or just write your products). C341 Br CH3NH2 CH3CH2OH CH₂OH Br CH3CH₂OH A Page 5 of Chapter 7: E2 SNI + E1arrow_forward
- Predict the MAJOR product(s) of each reaction or sequence of reactions. Show stereochemistry where applicable and draw out ALL stereoisomers that are formed as MAJOR products. For those with more than one reaction, show ONLY the final product(s) after all steps listed are performed (intermediate products will not be graded). Assume all reagents are in excess. 1) PBr3 2) N3 OH 1) HBr 2) CH;00arrow_forwardWrite the appropriate reagents, conditions and products for the following transformations, in a single step. OH II HNO, ? (1) H,SO,arrow_forwardOn acid-catalyzed dehydration, 1-butanol (CH3CH2CH2CH2OH) can be converted to 1-butene. Write out an equation for the reaction Assign each the appropriate symbol for the mechanism of the reaction (E1 or E2) Draw a suitable mechanism for the reactionarrow_forward
- 2. The following reaction results in two possible carbocation rearrangement products, each of which can be characterized by a change in the ring size. Give structures for both products. There is no need to show the mechanism of the reaction. HCI (conc)arrow_forwardGive the product/s for the following reaction and indicate what mechanism is involved in the formation of such product/s as SN1, SN2, E1, E2. CH3CH=CHCl + NaNH2arrow_forwardPredict the mechanism(s) (SN1, SN2, E1, E2) and major product(s) for each reaction.arrow_forward
- Predict the major and minor products that would be obtained from each of the following reactions. Give the mechanism (SN1, SN2, E1, or E2) by which each product is formed.arrow_forwardDraw the major product or products of each of the following reactions. Indicate whether the reaction occurs by an SN1, SN2, E₁, or E₂ mechanism on the line provided. Be sure to include stereochemistry in your answers where it is appropriate. mechanism H₂C CH3 Br Br CI OH CH3OH 60° H₂O NaSH 25° KOC(CH3)3 HOC(CH3)3, 100° acetone HCIarrow_forward) Provide a reaction mechanism for the following reactions and name the major product for each. HBr H,SO4 HO,arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
