
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
A concept map is to be drawn and the liters of
Concept introduction:
A mole is a basic unit used in the International system of units (SI). It is abbreviated as
Answer to Problem 18E
The concept map is shown below.
The liters of
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 1
The formula to calculate the number of moles of
The mass of
The molar mass of
Substitute the mass and molar mass of
The volume occupied by
The formula to calculate the volume occupied by
Substitute the volume of
Therefore, the liters of
The liters of
(b)
Interpretation:
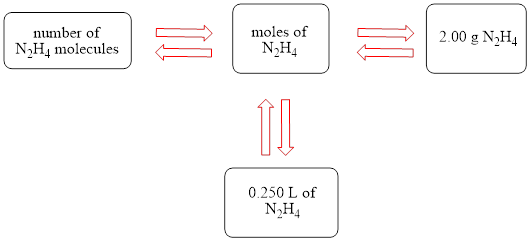
A concept map is to be drawn and the molecules of
Concept introduction:
A mole is a basic unit used in the International system of units (SI). It is abbreviated as
Answer to Problem 18E
The concept map is shown below.

The molecules of
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 1
The formula to calculate the number of moles of
The mass of
The molar mass of
Substitute the mass and molar mass of
The molecules present in
The formula to calculate the molecules occupied by
Substitute the molecules in
Therefore, the molecules of
The molecules of
(c)
Interpretation:
A concept map is to be drawn and molar concentration of the hydrazine solution in the solution in when
Concept introduction:
A mole is a basic unit used in the International system of units (SI). It is abbreviated as
Answer to Problem 18E
The concept map is shown below.

The molar concentration of the hydrazine solution is
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 1
The formula to calculate the number of moles of
The mass of
The molar mass of
Substitute the mass and molar mass of
The number of moles in
The formula to determine molarity is shown below.
Where
•
•
•
Substitute the value of number of moles and volume in equation (1).
The relation between
The unit factors are given below.
The unit factor to determine
Therefore,
Therefore, the molar concentration of
The molar concentration of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking (8th Edition)
- In a dilute solution of sodium chloride in water, the sodium chloride is the: a. solvent. b. solute. c. precipitate. d. reactant.arrow_forwardHow many milliliters of 0.865 M H3PO4 will contain the following? (a) 0.11 mol H3PO4 (b) 33.6 g H3PO4 (c) 4.68 x 1022 molecules of H3PO4arrow_forwardRefer to the oxygen concentration example in Sec. 1.7.2.(a) Given that nitrogen is lighter in weight than oxygen, is N2 concentration at 10 kmmore or less that 25% of the sea level N2 concentration?(b) What is the ratio of N2 concentration to O2 at 10 km? At sea level, the ratio is 4 to 1.arrow_forward
- If a container of liquid contains 60oz of solution, what is the number of ounces of pure acid if the given solution contains the following acid concentrations (a) 20% (b) 15% (c) 30% (d) 50%arrow_forwardConsider this question: What is the mass of solute in 200.0 L of a 1.556-M solution of KBr?(a) Outline the steps necessary to answer the question.(b) Answer the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the molar concentration of a lidocaine solution prepared by diluting 15. mL of a 2.0 M lidocaine stock solution to the mark in a 25 mL volumetric flask? include unitsarrow_forward
- What percent of water is in the compound Magnese (ii) chloride tetrahydrate?arrow_forward14) Which of the following terms best describes a carbonated beverage?(a) compound (b) heterogeneous mixture(c) homogeneous mixture (d) substance(e) none of the above show step solutions 15) Alum is used in styptic pencils to stop minor bleeding. If the formula is Al2(SO4)3 what is the total number of atoms in one formula unit of alum?(a) 10 (b) 12 (c) 14 (d) 17 (e) 2116) Using atomic notation, indicate the isotope having 25 p+, 30 n0,and 25 e-a. 2580Mn b. 2555Mn c. 5525Mn d. 2555Zn e. 3055Zn Show step by step solutions 17) Element X has two natural isotopes: X-6 (6.015 amu) and X-7 (7.016 amu).Calculate the atomic mass of element X given the abundance of X-7 is 92.5%.(a) 6.09 amu (b) 6.50 amu(c) 6.52 amu (d) 6.94 amu(e) 12.5 amu Show step by step solutions 18) Which of the following photons of visible light is most energetic?(a) blue (b) red(c) violet (d) yellow(e) all visible light photons have the same energy Show step by step solutions 19) Which element has the following…arrow_forward(e) a pure substance QUESTION 6 Write chemical equations for each of the following chemical and physical processes: (a) Neutralization of an aqueous solution of barium hydroxide by the hydronium ion (b) Reaction of 1 mole of aluminum with I2(s) to form aluminum iodide (c) Conversion of 1 mole of O2(g) to O3(g) (d) Dissolving C12H22011(s) (sugar) in water (e) Combustion of CH3OH(t) (f) Thermal decomposition of 1 mole of solid sodium azide to produce solid sodium and nitrogen gas (g) Photodissociation of hydrogen gas (h) Fusion of gold QUESTION 7 Convert the units below Use dimensional analysis where appropriatearrow_forward
- Sea water contains roughly 28.0 g of sodium chloride NaCl per liter. What is the molarity of sodium chloride in sea water?arrow_forwardCalculate what volume of the following solutions is required to obtain 0.261 mol of each solute. (a) 0.280 M AlCl3 L (b) 3.71 M HCl Larrow_forwardWhat is the mass of a 5.6 liter (STP) sample of CO2 gas?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning


