
(a)
Interpretation:
The stoichiometry concept map is to be drawn and the mass of reacted methane
Concept introduction:
Stoichiometry measures the amount of reactant and product consumed or formed in a
Answer to Problem 23E
The stoichiometry concept map is shown below.
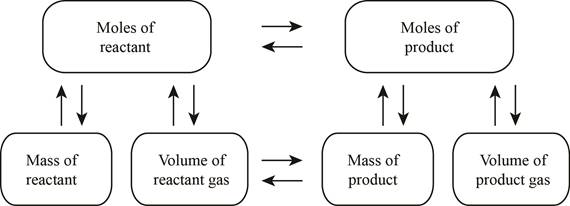
The mass of the reacted methane is
Explanation of Solution
It is given that
The stoichiometry concept map is shown below.
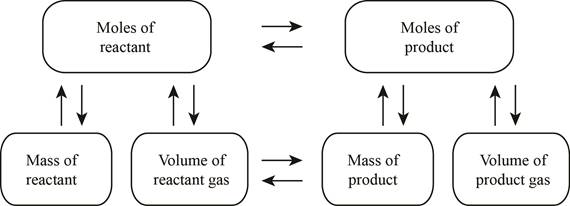
Figure 1
The chemical reaction (1) should be balanced first to calculate the mass of reacted methane.
The number of oxygen atoms is not equal on both sides. A coefficient of
The number of hydrogen atoms is not equal on both sides. A coefficient of
The balanced equation is shown below.
The mass of methane reacted is equal to the mass of
The molar mass of hydrogen is
The molar mass of oxygen is
Therefore, the number of moles of methane is calculated from the number of moles of water using a stoichiometric ratio as shown below.
For
The mass of methane reacted can be calculated from the number of moles of methane which is
The molar mass of carbon is
The molar mass of hydrogen is
The number of moles of methane can be calculated from the relation shown below.
The mass of methane for
Therefore, the mass of methane is
The stoichiometry concept map is shown in Figure 1. The mass of methane consumed in the reaction is
(b)
Interpretation:
The volume of carbon dioxide
Concept introduction:
Stoichiometry measures the amount of reactant and product consumed or formed in a chemical reaction. It gives the relationship between the reactants and products. Stoichiometry concept maps are used to determine the relation of reactant and product in terms of stoichiometry.
Answer to Problem 23E
The stoichiometry map is shown below.
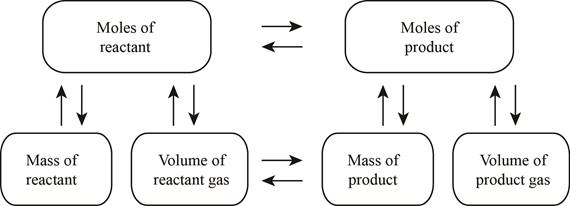
The volume of carbon dioxide produced at
Explanation of Solution
The stoichiometry concept mass is shown below.
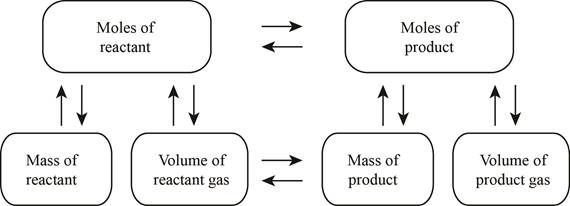
Figure 1
The balanced chemical reaction is stated in part (a) named as equation (2) is used to calculate the volume of
The equation (2) shows that 1 mole of methane is consumed to form 1mole of carbon dioxide.
Therefore, the volume for
Therefore, the volume of
The volume of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking (8th Edition)
- A power plant is driven by the combustion of a complex fossil fuel having the formula C11H7S. Assume the air supply is composed of only N2 and O2 with a molar ratio of 3.76:1.00, and the N2 remains unreacted. In addition to the water produced, the fuels C is completely combusted to CO2 and its sulfur content is converted to SO2. In order to evaluate gases emitted at the exhaust stacks for environmental regulation purposes, the nitrogen supplied with the air must also be included in the balanced reactions. a Including the N2 supplied m the air, write a balanced combustion equation for the complex fuel assuming 100% stoichiometric combustion (i.e., when there is no excess oxygen in the products and the only C-containing product is CO2). Except in the case of N2, use only integer coefficients. b Including N2 supplied in the air, write a balanced combustion equation for the complex fuel assuming 120% stoichiometric combustion (i.e., when excess oxygen is present in the products and the only C-containing product is CO2). Except in the case of use only integer coefficients c Calculate the minimum mass (in kg) of air required to completely combust 1700 kg of C11H7S. d Calculate the air/fuel mass ratio, assuming 100% stoichiometric combustion. e Calculate the air/fuel mass ratio, assuming 120% stoichiometric combustion.arrow_forward62 Ammonium dinitramide (ADN), NH4N(NO2)2, was considered as a possible replacement for aluminium chloride as the oxidizer in the solid fuel booster rockets used to launch the space shuttle. When detonated by a spark, AND rapidly decomposes to produce a gaseous mixture of N2,O2, and H2O. (This is not a combustion reaction. The ADN is the only reactant.) The reaction releases a lot of heat, so the gases are initially formed at high temperature and pressure. The thrust of the rocket results mainly from the expansion of this gas mixture. Suppose a 2.3-kg sample of ADN is denoted and decomposes completely to give N2,O2, and H2O. If the resulting gas mixture expands until it reaches a temperature of 100°C and a pressure of 1.00 atm, what volume will it occupy? Is your answer consistent with the proposed use of ADN as a rocket fuel?arrow_forwardIs there a difference between a homogeneous mixture of hydrogen and oxygen in a 2:1 ratio and a sample of water vapor? Explain.arrow_forward
- What is the mass of a 5.6 liter (STP) sample of CO2 gas?arrow_forwardAssuming constant conditions, how many milliliters of chlorine gas react to yield 1.15 LL of dichlorine trioxide? Cl2(g)+O2(g)→Cl2O3(g)arrow_forwardFor this equation, (NH4)2Cr₂O7(s) → Cr₂O3 (s) + N₂(g) + 4H₂O(g) An engineer has to calculate the volume of gases that are produced under standard temperature and pressure conditions, given that 1,458 g of ammonium dichromate will decompose. Select the three values needed to solve this problem. The molar mass of nitrogen gas. The molar mass of ammonium dichromate. The molar mass of water. The molar ratio from the balanced equation. Avogadro's number: 6.02e23 particles/mol. The STP molar gas volume: 22.4.L/molarrow_forward
- STARTING AMOUNT X Sodium and chlorine react according to the balanced chemical equation shown below. If the reaction is performed at STP, how many g NaCl are created if 38.2 g of sodium are reacted with an excess of chlorine gas? 70.90 ADD FACTOR x( ) Tap here or pull up for additional resources 22.99 g Na 15.0 2 58.44 Question 12 of 42 g NaCl Na(s) + Cl₂(g) → 35.2 0.0103 97.1 2 NaCl(s) 2 ANSWER 0.0284 45.98 g NaCl/mol mol NaCl 5.13 x 104 g Na/mol 1 RESET 2 mol Na 38.2 Submitarrow_forwardHow many mL of chlorine gas are required to produce 50.0 mL of hydrogen chloride gas?arrow_forwardNitric acid is produced fromnitrogen monoxide, which is in turnis prepared from ammonia by a process known as the Ostwald process, shown below. If 250. mL of oxygen reactswith 250. mL of ammonia, what mass(in g)of nitrogen monoxide will be producedat STP?arrow_forward
- The design of air-bag depends on stoichiometric precision. The following reaction takes place when the air-bag is inflated. 2 NaN3 (s) → 2 Na(s) + 3 N2 (g) 6Na(s) + Fe2O3(s) → 3NA2O(s) + 2Fe Assume that 43.4 L of nitrogen gas are needed to inflate an air bag to the proper size. (A) How many grams of NaN3 must be included in the air-bag to generate this amount of nitrogen gas? (The density of nitrogen gas at this temperature is 0.916 g/L). (B) How much Fe2O3 (in grams) must be added to the air-bag for this amount of NaN3? Use the following molar masses: N2 = 28.02 g/mol NaN3 = 65.01 g/mol Fe203 = 159.69 g/mol Type only the numerical answers in the answer box grams of NaN3 grams of Fe2O3 =arrow_forwardThe density of F2 gas is 1.70 g/L.How many moles of F2 gas are present in a 475 L sample of a gas mixture that is 4.00 % fluorine and 96.00 % helium?arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is not true: Question 23 options: Avogadro’s number is 6.02 x 10 23 “things.” 1 mole of gas occupies 22.4 L of volume at STP. An endothermic reaction produces heat. STP is represented by 760torr and 0oC.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





