
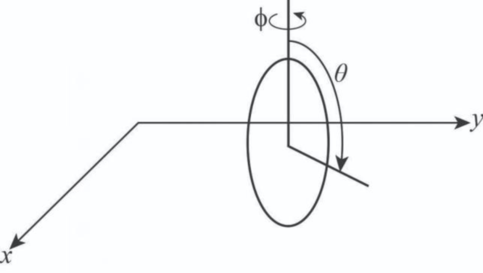
The generalized coordinates and description about the rolling disk.
Answer to Problem 7.1P
The generalized coordinates and description about the rolling disk are given.
Explanation of Solution
In order to describe the rolling of disk without slipping, four generalized coordinates are required. They are – x coordinate, y coordinate, angle
Equation of motion for the rolling disk is,
Here,
These equations are not integrable. Moreover, all the generalized coordinates cannot be combined into a single equation. Hence, the constraints are nonholonomic.
Conclusion:
Therefore, generalized coordinates and description about the rolling disk are given.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
- For Problem 8.16, how do I prove the relations and give the correct expressions?arrow_forward1. Consider the 2D motion of a particle of mass u in a central force field with potential V(r). a) Find the r, o polar-coordinate expression of the Lagrangian for this system and write down the corresponding Euler-Lagrange e.o.m.s. b) Note that the angular variable o is cyclic. What is the physical interpretation of the correspond- ing integral of motion? (For the definitions of the italicized terms see this link.) c) Solve for o in terms of this integral of motion and substitute the result into the Euler-Lagrange equation for r. Show that the result can be arranged to look like a purely 1D e.o.m. of the form dVef(r) (1) dr Identify in the process the explicit expression for Vef(r), which will depend among other things on the integral of motion. d) Take now k V (r) = with k > 0 to be an attractive electrostatic/gravitational-type potential. Sketch the profile of the corresponding effective potential function Vef(r). Find the equilibrium solution for the correspond- ing e.o.m. (1). What…arrow_forwardThe dynamics of a particle moving one-dimensionally in a potential V (x) is governed by the Hamiltonian Ho = p²/2m + V (x), where p = is the momentuin operator. Let E, n = of Ho. Now consider a new Hamiltonian H given parameter. Given A, m and E, find the eigenvalues of H. -ih d/dx 1, 2, 3, ... , be the eigenvalues Ho + Ap/m, where A is a %3|arrow_forward
- A disk of mass M and radius R rolls without slipping down a fixed inclined plane that makes an angle a with the horizontal plane. (see figure). RPO P.E = 0 (a) Write down the constraint equations and determine the number of degrees of freedom s. (b) Choose a convenient generalized coordinate. (c) Write down an expression for the Lagrangian of rolling ball. Given: the moment of inertia of the ball about its center is I, = }MR² (d) Calculate the generalized momenta.arrow_forwardFor each of the following vector fields F , decide whether it is conservative or not by computing the appropriate first order partial derivatives. Type in a potential function f (that is, Vf = F) with f(0,0) = 0. If it is not conservative, type N. A. F (x, y) = (4x – 2y) i+ (-2x + 12y) j f (x, y) = B. F (x, y) = 2yi+ 3xj f (x, y) = C. F (x, y) = (2 sin y) i + (–4y + 2x cos y) j f (x, y) = Note: Your answers should be either expressions of x and y (e.g. "3xy + 2y"), or the letter "N"arrow_forward(e) v,y &+(2xy+)9+2yz &. Problem 16 Sketch the vector function %3D and compute its divergence. The answer may surprise you...can you explain it?arrow_forward
- Here are some statements/results involving matrices and vectors. Select all that are correct. All are given somewhere in RHB secs. 8.2 to 8.8 Negative marking applies. Select one or more: a. For two square matrices A and B: Tr(AB) = Tr(BA) b. (AB)¹ = B¹A¹ C. If A and B are diagonal matrices (i.e., all off-diagonal terms are zero), then AB=BA. Od. The inner product of two vectors can be written in terms of the Hermitian conjugate as follows: (a/b) = a¹b e. For square matrices A, B, C, D: Tr(ABCD)=Tr(DABC).arrow_forwardPlease solve part d,e,f Consider a particle of mass m constrained to move on the surface of a cone of half-angle a as shown in the figure below. (a) Write down all constraint relations in cylindrical coordinates. (b) Show that the number s of degrees of freedom is eaual 2. (c) Choose s convenient generalized coordinates. (d) Obtain expressions for the kinetic energy, potential energy. and Lagrangian function in spherical generalized coordinates. (e) Determine if any coordinate(s) are ignorable (f) Obtain expressions for the generalized momenta, m (g) Write down the Lagrange equations of motion.arrow_forwardA pendulum hangs from a fixed point, but the pendulum itself is a spring with a constantk and length I Assume that the whole thing moves in the vertical plane. How many connections are there and how many generalized coordinates? Give the Lagrangian the equation of motion. Calculate the equilibrium position. Argue why it is a stable equilibrium. Calculate the normal vibration frequency.arrow_forward
- Our unforced spring mass model is mx00 + βx0 + kx = 0 with m, β, k >0. We know physically that our spring will eventually come to rest nomatter the initial conditions or the values of m, β, or k. If our modelis a good model, all solutions x(t) should approach 0 as t → ∞. Foreach of the three cases below, explain how we know that both rootsr1,2 =−β ± Sqrt(β^2 − 4km)/2mwill lead to solutions that exhibit exponentialdecay.(a) β^2 − 4km > 0. (b) β^2 − 4km =0. (c) β^2 − 4km >= 0.arrow_forwardU sing the rules of B olo gnese algebra Demoreken's theorem, s implify the following. Booleah ex pression to the sim plest form and then draw the logical circle before simplification a fter simpiification an d the truth table (Ā + ē ).(B+ Ĉ ).(A+B +é)arrow_forwardAssume that you do not know about the kinetic energy or Newton’s Laws of motion. Suppose instead of deriving the Euler-Lagrange equations, we postulate them. We define the basic law of mechanics to be these equations and ask ourselves the question: What is the Lagrangian for a free particle? (This is a particle in empty space with no forces acting on it. Be sure to set up an inertial reference system.) Explain why, on very general grounds, L can not be a function of x, y,and z. It also can not depend on the individual coordinates of velocity in any way except as a function of the magnitude of the velocity: v2 = vx2 + vy2 + vz2. On what assumption about the properties of space does this depend?arrow_forward
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
