
Find the distance a.
Answer to Problem 7.148P
The distance a is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the cable AB is
The value of angle
The collar at A is slides freely and the collar at B is prevented from the moving.
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the cable assembly as in Figure 1.
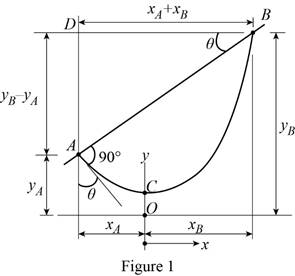
Refer Equation 7.16 in the textbook.
Write the equation of the catenary cable as follows;
Differentiate the equation with x;
The slope at point A is;
The length of the portion AC is;
The length of the portion CB is;
Find the distance
Substitute 10 ft for L,
Find the distance
Find the distance
Consider the triangle ABD;
Find the value of
Find the distance a using the relation.
Use the trial and error procedure to find the value of a.
Consider the value of c and for the given value of
Find the angle
Trial 1:
Consider a trial value of 1.60 ft for c.
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and 1.410 ft for
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and 1.410 ft for
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and 3.777 ft for
Substitute 1.410 ft for
The calculated value of
Trial 2:
Consider a trial value of 1.70 ft for c.
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and 1.498 ft for
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and 1.498 ft for
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and 3.891 ft for
Substitute 1.498 ft for
The calculated value of
Trial 3:
Consider a trial value of 1.8652 ft for c.
Substitute 1.8652 ft for c and
Substitute 1.8652 ft for c and 1.644 ft for
Substitute 1.8652 ft for c and 1.644 ft for
Substitute 1.8652 ft for c and 4.064 ft for
Substitute 1.644 ft for
The calculated value of
Therefore, the value of c is 1.8652 ft.
Substitute 2.638 ft for
Therefore, the distance a is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- a A |dx| 30° The support bracket shown is used to transport a cylindrical can from one elevation to another. Knowing that µs = 0.12 between the can and the bracket, determine the smallest ratio h/d for which the can will tip over before sliding.arrow_forwardThe uniform 10 kg rod AB is supported by a ball and socket joint at A and by the cord CG that is attached to the midpoint G of the rod. Knowing that the rod leans against a frictionless vertical wall at B and that the tension in the cord CG, TCG=52.1 N, determine the following, Which of the following best approximates the moment of the weight of the structure about A? Choices: (7.36i + 29.4k) N-m(7.36i + 29.4j) N-m(29.4i + 7.36k) N-m(29.4i + 7.36j) N-marrow_forwardThe pipe ABCDE is supported by ball-and-socket joints at A and D and by cable ECF that passes through a ring C with negligible friction and is attached to hooks at E and F. Knowing that the frame supports a uniformly distributed load of 1500 N/m along segment AB, do the following.1) Shows the correct vector representation of the resultant of the two tension forces acting at ring C. Note that T_CF = T_CE = T2) Explain along which line/axis you can sum moments to generate an equilibrium equation with only the magnitude of the tension force as the unknown. Explain your choice.3) Find the magnitude of the tension force.arrow_forward
- A 500-ft-long aerial tramway cable having a weight per unit length of 2.8 lb/ft is suspended between two points at the same elevation. Knowing that the sag is 125 ft, find (a) the horizontal distance between the supports, (b) the maximum tension in the cable.arrow_forwardIn order to unscrew the tapped faucet A, a plumber uses two pipe wrenches as shown. By exerting a 40-lb force on each wrench, at a distance of 10 in. from the axis of the pipe and in a direction perpendicular to the pipe and to the wrench, he prevents the pipe from rotating, and thus avoids loosening or further tightening the joint between the pipe and the tapped elbow C. Determine (a) the angle θ that the wrench at A should form with the vertical if elbow C is not to rotate about the vertical, (b) the force-couple system at Cequivalent to the two 40-lb forces when this condition is satisfied.arrow_forward7.7 and 7.8 A half section of pipe rests on a horizontal surface as shown. Knowing that the half section of the pipe has a mass of 9 kg and ne- glecting friction between the pipe and the surface, determine the internal forces at point J. 150 mm Fig. P7.8arrow_forward
- In order to unscrew the tapped faucet A , a plumber uses two pipe wrenches as shown. By exerting a 40-lb force on each wrench at a distance of 10 in. from the axis of the pipe and in a direction perpendicular to the pipe and to the wrench, he prevents the pipe from rotating, and thus he avoids loosening or further tightening the joint between the pipe and the tapped elbow C . Determine (a) the angle 0 that the wrench at A should form with the vertical if elbow C is not to rotate about the vertical, (b) the force-couple system at C equivalent to the two 40-lb forces when this condition is satisfied.arrow_forwardIf dC, = 15 ft. determine (a) : the distances dB and dD, (b) the inuximum tension in the cable.Fig. 7.99arrow_forwardKnowing that the radius of each pulley is 150 mm, that a = 20°, and neglecting friction, determine the internal forces at (a) point J, (b) point K.arrow_forward
- Collar A is connected as shown to a 50-lb load and can slide on a frictionless horizontal rod. Determine the magnitude of the force P required to maintain the equilibrium of the collar when (a) x = 4.5 in., (b) x =15 in. B C 20 in. 50 lb P Aarrow_forwardA container of weight W is suspended from ring A. Cable BAC passes through the ring and is attached to fixed supports at B and C. Two forces P = Pi and Q = Qk are applied to the ring to maintain the container in the position shown. Knowing that W = 542 N, determine P and Q. (Hint: The tension is the same in both portions of cable BAC.) 150 mm 140 mm B 240 mm 130 mm 420 mm P Warrow_forwardMp Fig. P8.126 8.127 Solve Prob. 8.126 assuming that u = 75°. B 8.128 The 10-lb bar AE is suspended by a cable that passes over a 5-in.- radius drum. Vertical motion of end E of the bar is prevented by the two stops shown. Knowing that m, = 0.30 between the cable and the drum, determine (a) the largest counterclockwise couple M, that can be applied to the drum if slipping is not to occur, (b) the corresponding force exerted on end E of the bar. A E 10 lb 5 in. 5 in. 3 in. Fig. P8.128arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





